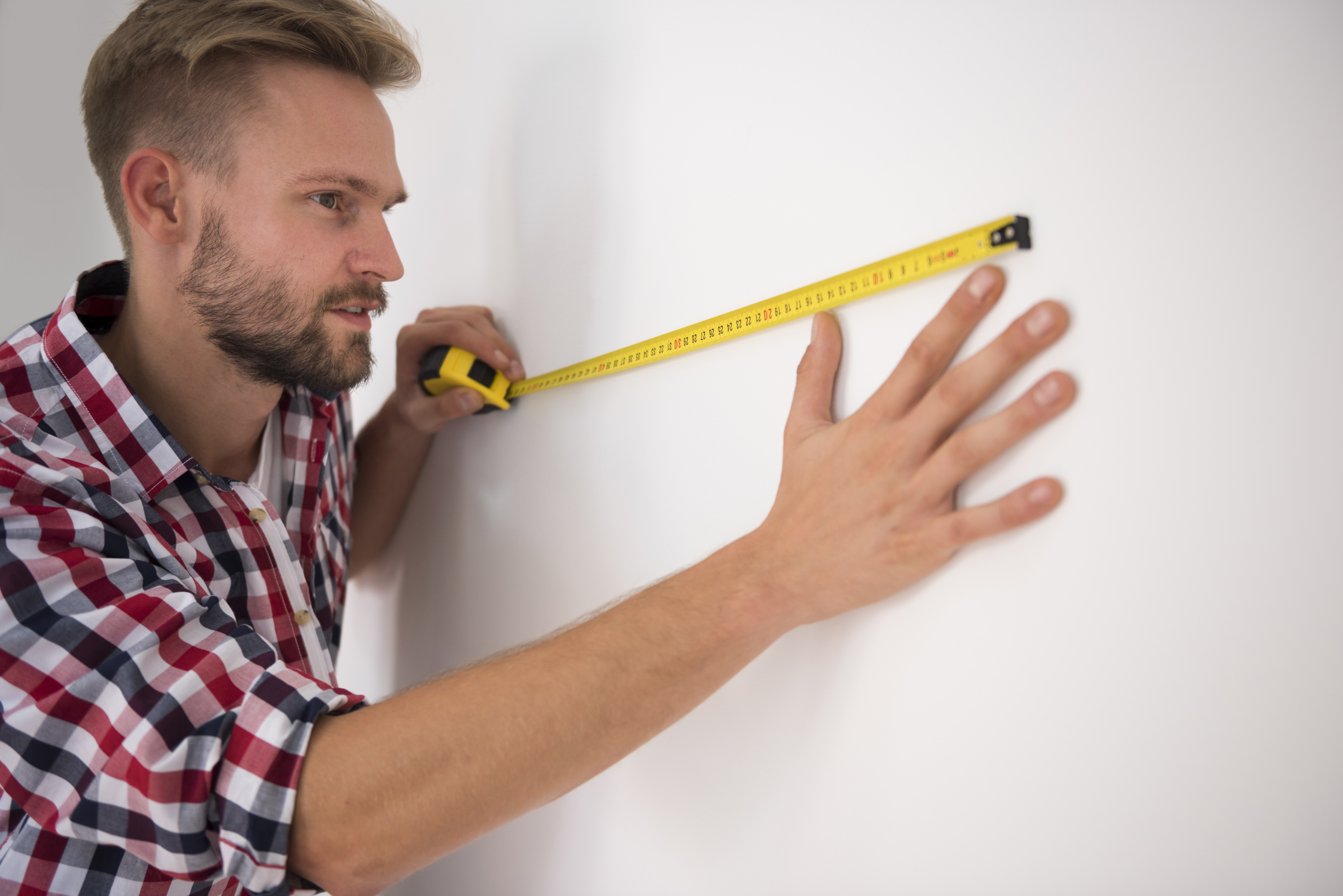
How to calculate the number of tiles for a wall is a question posed by anyone planning to renovate a bathroom, kitchen, or another room. Properly estimating the number of tiles needed saves time, money, and the stress of running out of materials during installation. In this article, we will show you step by step how to calculate the number of tiles needed, including the surplus and the specifics of the room.
What will you learn from this article?
Before laying tiles on the wall, it is necessary to correctly calculate how many will be "consumed" by the related work. Therefore, from our text, you will find out:
- How and with what to correctly measure the wall.
- How many surplus tiles you will need.
- What is involved in laying tiles.
Measuring the wall surface
To calculate the number of tiles for a wall, you need to precisely measure the surfaces that are to be covered with tiles. The wall surface area is expressed in square meters, which simplifies later calculations. Here's what to do step by step:
- Measure the walls – for this we recommend using a tape measure or measuring tape to determine the height and width of each wall. For example, if a wall is 2 m high and 3 m wide, its area is 2 m × 3 m = 6 square meters.
- Subtract areas not covered with tiles – such as skirting boards, doors, windows, or other elements, like mirrors, that will not be covered with tiles. Therefore, measure their dimensions and subtract their area from the total wall area. For example, a window measuring 1 m × 1 m is 1 m², so subtract 1 m² from 6 m², leaving 5 m².
- Add up the areas of all walls – if planning to tile more than one wall, add the areas of all walls to get the total wall area in square meters.
How to calculate how many meters of tiles you need?
Once the wall area is determined, consider how many tiles you need for that area. This requires:
- Checking the dimensions of the tiles – tiles come in different sizes, e.g., 120 × 60 cm (1.2 m × 0.6 m). To calculate the area of one tile, multiply its dimensions: 0.3 m × 0.6 m = 0.72 m²;
- Dividing the wall area by the area of one tile – if you have 5 m² of wall, divide 5 m² by 0.72 m², resulting in approximately 6.94 tiles. Always round up, so in this case, 7 tiles are needed;
- Allowing for a surplus – experts recommend adding a 10-15% surplus for losses, cuts, or damages. In our example, 7 tiles × 1.1 (10% surplus) = about 8 tiles.
What surplus of tiles to buy when finishing the interior?
It is standard to add:
- 10% surplus for simple layouts (e.g., classic horizontal arrangement);
- 15% surplus for diagonal, herringbone layouts, or complicated patterns where more tiles require cutting;
- Additional surplus for large projects or irregularly shaped tiles.
Although our article focuses on walls, it is worth mentioning that calculating the number of tiles needed for the floor can be done similarly. The process is almost identical:
- measure the floor area (length × width),
- subtract areas that will not be covered by floor tiles, e.g., under fixed furniture, as well as the planned width of the joint,
- calculate the number of tiles needed by dividing the floor area by the area of one tile and adding the surplus.
The specifics of tile laying on walls
Laying tiles on walls differs from floors due to the need to account for openings (e.g., for sockets, switches) and aesthetics. Therefore, accurate measurements are crucial: Always measure each wall separately because even small differences in dimensions can affect the quantity of tiles. Moreover, if planning to lay tiles in a herringbone pattern or with decor, calculate how many tiles are needed with a larger surplus (15-20%) because the cuts will be more complex. Remember also that for niches, alcoves, or sloped areas, each piece needs to be measured precisely to accurately determine the area of the walls.
Tile calculator
To find out how many tiles per square meter, divide 1 m² by the area of one tile. For example:
- tile 30 × 30 cm (0.3 m × 0.3 m = 0.09 m²): 1 m² ÷ 0.09 m² ≈ 11.11 tiles, so 12 tiles per m² rounded;
- tile 60 × 60 cm (0.6 m × 0.6 m = 0.36 m²): 1 m² ÷ 0.36 m² ≈ 2.78 tiles, so 3 tiles per m².
Errors in calculating the required number of tiles can lead to either a shortage or an excess of materials. To avoid them, you should:
- Take precise measurements, using accurate measuring tools and recording the dimensions;
- Factor in cuts, remembering that tile cutting generates waste, so always buy more tiles;
- Check the dimensions of the tiles, ensuring you know the exact dimensions of the tiles before calculations.
- Decide whether the tiles will be laid straight or in a more complex pattern, which will affect the surplus.
Calculating tiles – summary
It is crucial to accurately measure the wall area in square meters, subtract areas not covered by tiles, and calculate the number of tiles needed based on their size. Calculate how many tiles are needed, factoring in a 10-15% surplus for cuts and losses. Floor tiles also require a similar approach but differ in installation specifics. With our tips, anyone can avoid costly mistakes when purchasing finishing materials. Just like when installing a recessed shower faucet.